Render Loop
The first thing we need to do is to familiarize ourselves a bit with Raylib_cs. Replace the content of Program.cs with the following code:
using System.Numerics;
using Raylib_cs;
using static Raylib_cs.Raylib;
static Texture2D GenCheckedTexture(int size, int checks, Color colorA, Color colorB)
{
Image imageMag = GenImageChecked(size, size, checks, checks, colorA, colorB);
Texture2D textureMag = LoadTextureFromImage(imageMag);
UnloadImage(imageMag);
return textureMag;
}
// set a hint for anti-aliasing
SetConfigFlags(ConfigFlags.Msaa4xHint);
// initialize a 1200x800 px window with a title
InitWindow(1200, 800, "BoxDrop example");
// dynamically create a plane model
Texture2D texture = GenCheckedTexture(10, 1, Color.LightGray, Color.Gray);
Model planeModel = LoadModelFromMesh(GenMeshPlane(10, 10, 10, 10));
SetMaterialTexture(ref planeModel, 0, MaterialMapIndex.Diffuse, ref texture);
// create a camera
Camera3D camera = new ()
{
Position = new Vector3(-20.0f, 8.0f, 10.0f),
Target = new Vector3(0.0f, 4.0f, 0.0f),
Up = new Vector3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f),
FovY = 45.0f,
Projection = CameraProjection.Perspective
};
// 100 fps target
SetTargetFPS(100);
// simple render loop
while (!WindowShouldClose())
{
BeginDrawing();
ClearBackground(Color.Blue);
BeginMode3D(camera);
DrawModel(planeModel, Vector3.Zero, 1.0f, Color.White);
EndMode3D();
DrawText($"{GetFPS()} fps", 10, 10, 20, Color.White);
EndDrawing();
}
CloseWindow();
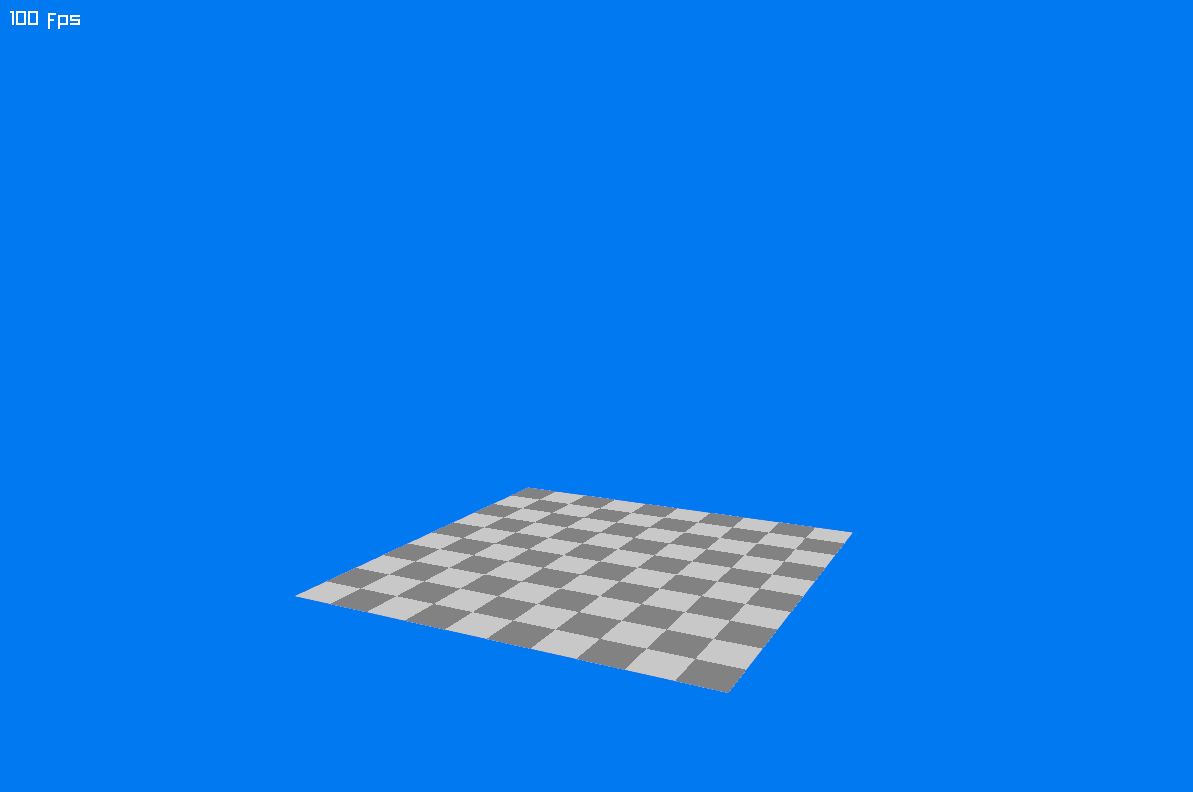
Running your program should now display a plane:
We will add some physically simulated boxes in the next chapter.